TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Micro Update Service (MUS)
Micro Update Service (MUS)
The Micro Update Service (MUS) enables external processes such as SCCM build scripts to update ManagementStudio records (including Users, Applications, and Devices) by writing specially formatted files to a monitored network location. This method allows integration with business processes without requiring direct interaction with the ManagementStudio API.
The MUS Endpoint extends this functionality by providing an HTTP endpoint for external services to POST update files directly to MUS. An access key is required for authentication, and only a single active key is supported at any given time.
Requirements:
- MUS Service requires ManagementStudio version 2022.0.8.5 or higher.
- MUS Endpoint requires ManagementStudio version 2026.16.1.1 or higher.
MUS Settings
The following options are available for configuring MUS:
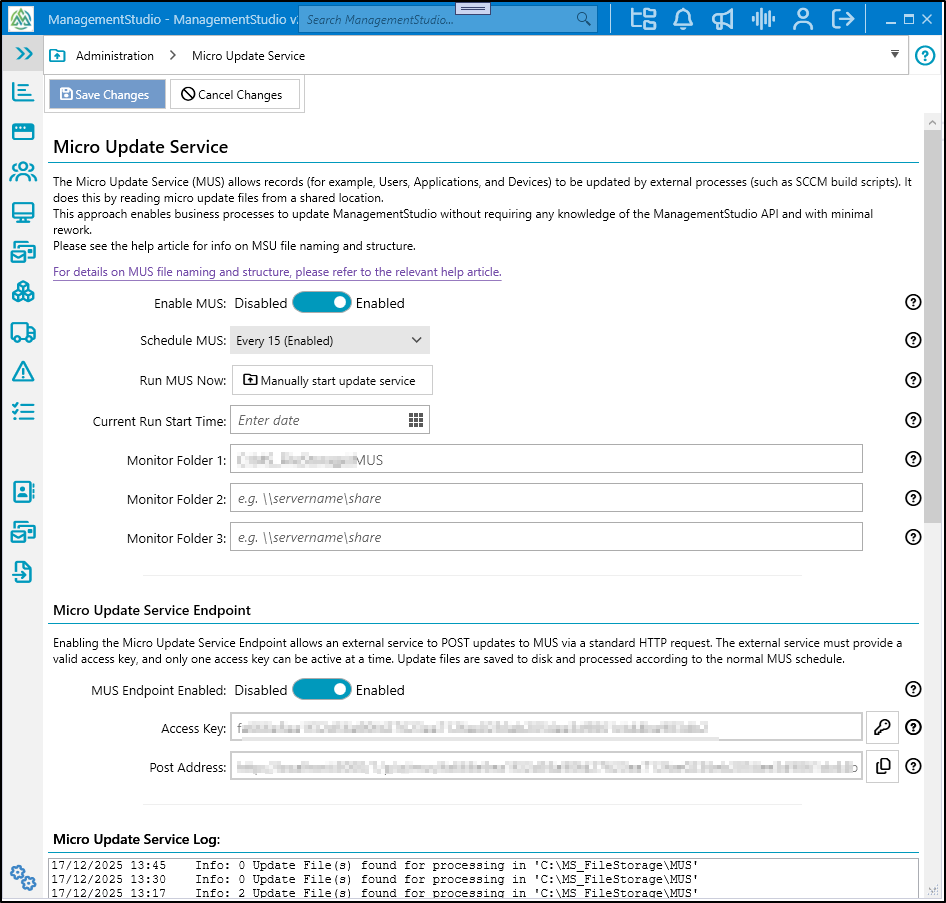
Enable MUS
Enable or disable the Micro Update Service.Schedule MUS
Configure one or more scheduled times for MUS to process queued files.Run MUS Now
Manually trigger MUS to process any pending files immediately.Current Run Start Time
Displays the start time of the ongoing MUS job. Blank if no job is running.Monitor Folder 1, 2, 3
Set local or UNC paths to monitor for new MUS files.MUS Endpoint Enabled
Enable or disable the HTTP MUS Endpoint for updates via POST requests.Access Key
Generate an access key for HTTP submissions. Only one key is active at any time. Generating a new key invalidates the previous key and may require services to update their configuration to prevent401 Unauthorizederrors.Post Address
The MUS Endpoint URL for POST submissions.Log
Displays recent log entries related to the MUS service.
File Format
To submit an update via MUS (file or endpoint), create a text file that:
- Has a filename starting with
MUS_ - Is uniquely named (recommended)
- Specifies a ManagementStudio record to update
- Includes at least one field or custom field value to update, each on its own line
Filename Example
A valid filename:
MUS_DT113421_01.txt
- Starts with
MUS_ - Includes an identifier (e.g., computer name)
- Uses a unique suffix (such as
_01or timestamp) to avoid overwriting
Note: Processed files are archived. If filenames are not unique, new files overwrite previous versions.
Folder Monitoring Considerations
When running multiple MUS instances (e.g., across separate projects), ensure each monitors a separate folder.
Examples:
\\ServerName\Share\ProjectName
\\DataServer01\Incoming\MergerProject
\\DataServer01\Incoming\HardwareRefreshProject
File Content Structure
Identifying the Target Record
The first line must identify the ManagementStudio object to update, using the format:
ID:IdType:TargetName
IdType: The identifier type (e.g.,Hostname,SamAccount)TargetName: The name or value for the target
Updating Fields
Subsequent lines update fields or custom fields. Each follows:
TargetType:Target:NewValue
Each field update must be on a separate line.
MUS Endpoint Examples
External systems can POST MUS files using PowerShell or other tools.
Example 1: Access Key in URL
$musUrl = "http://MS-Server/1/p/a/mus/fa6......"
$update = @'
ID:Hostname:PC00045
CFId:14801:True
CFId:14802:This is the error message from the task sequence
'@
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $musUrl -Method Post -Body $update -ContentType 'text/plain; charset=utf-8'
Example 2: Access Key in Header
$musUrl = "http://MS-Server/1/p/a/mus"
$accessKey = 'fa6...'
$update = @'
ID : SamAccount : global\jdoe
Field: Email: jdoe@global.com
'@
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $musUrl -Method Post -Body $update -ContentType 'text/plain; charset=utf-8' -Headers @{ accessKey = $accessKey }
SCCM Command-Line Examples
Basic Example
Create a MUS file on a network share:
cmd.exe /c "(echo ID:Hostname:%COMPUTERNAME% & echo CFId:100:Upgrade Initiated & echo CFId:110:Task Sequence Completed) > \\ServerName\Share\MUS_%COMPUTERNAME%.txt"
Including Time for Unique Filenames
cmd.exe /c "(echo ID:Hostname:%COMPUTERNAME% & echo CFId:100:Upgrade Initiated & echo CFId:110:Task Sequence Completed) > \\ServerName\Share\MUS_%COMPUTERNAME%_%time:~1,1%%time:~3,2%%time:~6,2%.txt"
Updatable Modules
| Module | ID Type |
|---|---|
| Applications | AppId, App-CustomerId |
| User Migrations | MigrationId, Domain\SamAccount, Email, UserAdSid |
| Device Migrations | DeviceId, Hostname, SmBiosGuid |
| Mail Migrations | MailId, MailName1, MailName123, MailAdSid |
| Bespoke Migrations | BespokeId, BespokeName1, BespokeName123, MailAdSid |
| Deployment Units | DeployUnitId, DeployUnitName |
| Target Type | TargetField | New Value Example |
|---|---|---|
| ID | AppId, MigrationId, Hostname, ... | 1000, 'PC0001', 'global\rhynes' |
| Field | AppVendor, AppName, FirstName, ... | |
| CFPath | CF Path | 'Form\Section\Field' |
| CFId | CF Field Id | 1234 |
| Process | Process | 'Process Name\Sub Process' |
| Note | Note | Some note text |
| Option | CreateIfNotFound | true |
Special Characters:
- Use
\:to escape:in values.- Use
\nto represent a new line in field values.- When writing date/time, escape the colon in the time portion, e.g.:
CFID:999: 2024-05-09 02\:03
Example Text Files
Update Device from SCCM TS
ID:Hostname:PC00045
CFId:14801:True
CFId:14802:This is the error message from the task sequence
Update Migration Record
ID:MigrationID:8901
CFId:153:ThisData2`r`nThatData2`r`nMoreData8
Update a User
ID : SamAccount : global\jdoe
Field: Email: jdoe@global.com
Create a New App and Move to a Process
Id: App-CustomerId: 12345
Option: CreateIfNotFound: true
Field: AppVendor: Adobe
Field: AppName: New Reader
Field: AppVersion:2021.011.20039
Process: 2. Discovery
Note: Note: Created from ServiceNow support ticket
Security
Because MUS processes anonymous text files from monitored folders, secure these shares appropriately:
- Only permit approved Active Directory (AD) accounts to write files to the folder.
- Block write access for all other accounts.
Practical example:
If MUS is used to process files generated by an SCCM Task Sequence, only the following should have write access:
- The SCCM Active Directory service account
- The ManagementStudio service account
All other users and accounts should be denied write access.
Further Support
For further assistance, visit the ManagementStudio Service Desk to search the knowledge base or raise a support ticket.
Was this article helpful?
That’s Great!
Thank you for your feedback
Sorry! We couldn't be helpful
Thank you for your feedback
Feedback sent
We appreciate your effort and will try to fix the article